Abstract
When we talk about internal clock, we actually refer to the circadian rhythm of higher animals and plants. Sensing the cycling environmental factors (light and temperature, etc.), circadian clock allows organism to behave accordingly and reguarly. This year, we develop a plug-in for microbes, a system that can build up an internal clock for microbes and guide them to live regularly as well as to work efficiently. Also, we could insert this system into dangerous strains and endue life span, they are doomed to die before causing any biohazard. Flip units based on recombinase system are introduced in our system. One flip unit is able to calculate a specific period of time, while several flip units form one time cycle. So, when we combine several time cycles together, a timer is constructed. Different flip unit assemblies creat distinctive time cycles, forms different kinds of timers. We believe this system will be of great significance to biological devices with time-related concepts.
Background
Meanings of Timer in Microbes
It is well known that the internal clock is of great significance to human life. The time rhythm let people work and rest regularly, which keeps us healthy and energetic. However, in microbes, especially prokaryotic organism, we could hardly find a strain with rhythm.
Actually, adding rhythm into microbes is a meaningful thing, by which would provide us a brand new technology platform or control system. This year, we hope to construct a rhythm device with time limit. As follows, we will use 3 simple hypothetical cases to illustrate its future application potentials.
a. Industry application of microbial rhythm
When it comes to microbial industry, we often find restrictive reaction space and strict operations necessary, since in the current industrial production, without autonomic consciousness, microorganisms could only behave under stress. So, if we want to express several proteins in turn, this limit determines that we have to add a new inducer once in a while to initiate the expression of a new gene. However, once microbes have autonomic rhythm and the concept of time, any operation with timing demands could be done in a autonomic way. We could make bacteria express proteins in chronological order, or realize certain behaviors by periodic expression, and then, apply to industrial mass production.

b. Advantages of adding microbes rhythm in therapy
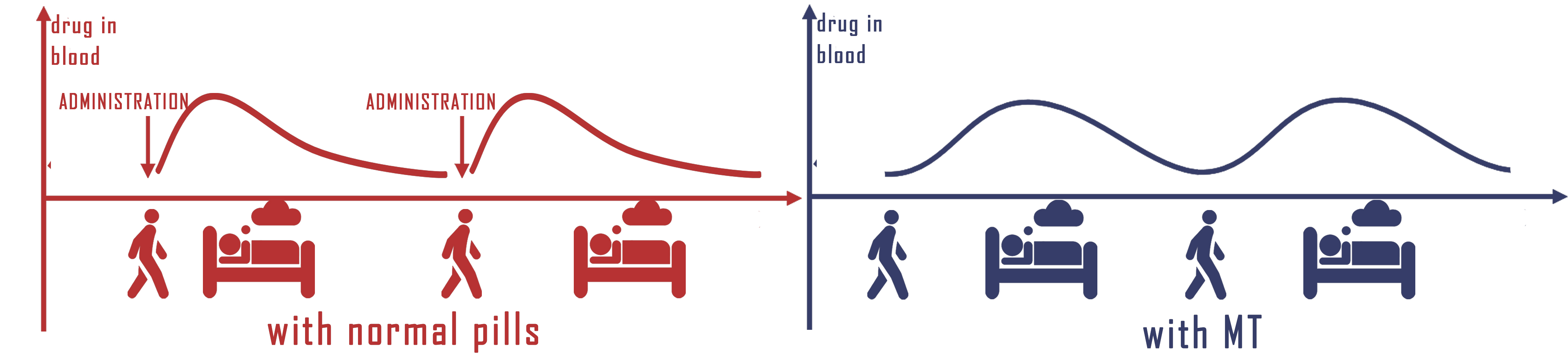
Frankly speaking, almost everyone has the experience of not taking medicines on time. In fact, patient compliance has always been a significant problem effecting the therapeutic results. It is common that a patient has to take different pills in different time each day, using the engineered E.coli to secrete medicines with rhythm would greatly simplify the medications and improve drug therapy compliance, therefore, ensures the curative effect. What's more, long-termed treatments would become available for any diseases or symptoms associated with time.
c. Meaning of hereditary time limits
By far, many iGEM projects are based on the construction of strains used in medical treatments, but planting living microorganisms into human body has great potential safety hazards. However, if the microbes have time limit devices triggered by inverted modules which would let microbes commit suicide in calculated time, we might be able to use them to treat human. Such microorganisms would die naturally after function, and since the condition of inverted modules is hereditary, the suicide process of the group would not be disturbed by cell fission, which would avoid most of the potential hazards. Time limits are also capable of more sophisticated applications, for example, timed initiation of gene expression. In the future biological industries and biomedical fields, its prospects are almost limitless.
Recombinase System
The design of our project is mainly based on recombinase system, a complete recombinase system comprises of a kind of recombinase and its corresponding recombination target sites(RTSs). Here are the recombinase system's principle.

a. when two RTSs are in the same direction, the sequences between will be cut out and form a circular DNA under the performances of corresponding recombinase. b. when two RTSs are in reverse direction, the sequences between will be flipped under the performances of corresponding recombinase.
Description
Matching and Testing
The goal of our group is to provide a systematic solution to Micro-timer construction, which includes optimization of synthetic elements and measurement of invertase module timing length. Hence, we developed a real-time invertase dynamics testing system to observe the performance of each combination of different elements. The real-time invertase dynamics testing system consists of two different plasmids in E. coli, namely pInv-gen and pInv-rep. pInv-gen generates invertase-EGFP fusion protein when induced; pInv-rep produces mcherry signal when inverted by invertase-EGFP. The dynamic pattern of the two signal can be mathematically analyzed, and the interval between bursts of green and red signals indicate the timing length of the invertase module. Furthermore, we tested effects of promoter, fusion sites, and ssra-tag in this system, and these elements are extremely helpful to enhance the performance of the device. With this system, we successfully tested the activity of invertases including Cre, Vika, Scre, Vcre, Dre, and Flp.
Prokaryotic Timer
Our group aims at constructing an innovative timer in bacterial system based on recombinase-triggered flipping, in which we attempted to construct several parts and devices served for relevant function. ECFP, mCherry and GFP were detected in different time scale to exhibit wholly flipping process. We developed a creative joining method called "2A" assembly to cope with plentiful scattered DNA fragments, when, at last, we managed to get our circuits tested by certain ways on its availability.
Telomeric Timer
Telomeric timer,also called Micro-timer 2.0, is designed to endue microorganisms with programed life span based on the cell cycle specific promoter (in eukaryotes) )or other cell division related promoter (in prokaryotes). In this system, the flanking RTSs are of same direction, enabling the sequences between them to be excised by specific recombinases, causing deletion of DNA fragments. With every cell division, this device will sequentially truncate a part of the sequence and finally lead to cell death when there is no more sequences to be truncated, working like a telomere.
Eukaryotic Timer
Eukaryotic timer,also called Micro-timer 3.0, uses recombinases from Ser family such as Bxb1, which typically catalyze site-specific recombination between an attachment site on the infecting phage chromosome (attP) and an attachment site in the host chromosome (attB) in natural system. The resulting integration reaction inserts the phage genome into the host chromosome bracketed by newly formed attL and attR (LR) sites. When attB and attP are engineered to be opposite BP sites, the integrase catalyzes the inversion of sequences flanked by BP sites, changing BP sites into LR sites, and will not revert the DNA flanked by LR sites.
In the design of Micro-timer 3.0, each inverted promoter flanked by BP sites is at the downstream of an inverted reporter gene and followed by a ser integrase gene. The reporter i(inverted reporter gene)-attP-promoter i-attB-integrase unit is defined as a counting motif, named eukaryotic timer integrase motif (EIM). EIM can be inserted into different sites of chromosomes, creating a large scale and multi-level system in eukaryotes.
The circuit can be programmed to record time by counting a specific type of events such as the expression of cyclins. Once the motifs are activated, the downstream expression can work automatically and will not be terminated or reset by the hosts themselves, which is the reason why we believe that such a system can imprint “the same time” on microbes derived from a monoclone.
To make better use of the bxb1 integrase, we improved the biobrick BBa_K1039003 submitted by iGEM2013-Waterloo, optimizing it to match RFC 25 standard (BBa_K1641900) and thus it can be applied on 3A-fusion-assembly.
Registry Contribution
New application of Cre (BBa_K1179058) and its detailed measurement.
Although the data in the iGEM Registry is pretty large for iGEMers to obtain most common information, there is limited material about recombinases, and less about the invertase activity. Hence we tried our best to gather information about one of the most commonly used recombinases – Cre.
BBa_K1179058 is a Cre CDS provided by team iGEM13_MIT, and all of our experiments about cre is established using this sequence. We developed a real-time invertase dynamics testing system based on BBa_K1179058, and confirmed its functionality as an invertase. Further, we measured the dynamics pattern of its enzymatic activity and discovered some interesting property of this invertase.
In sum, we not only provided a new application for this part, but also measured the detailed dynamics pattern of this recombinase.
RFC25 optimization of bxb1integrase (BBa_K1039003)
The bxb1 integrase part has been submitted by iGEM2013-Waterloo (BBa_K1039003), but it does not match the RFC25 standard and thus can not be applied on fusion via 3A assembly. In SYSU-CHINA 2015, we modified the bxb1 gene to make it match the RFC25 standard.




