Difference between revisions of "Team:Bielefeld-CeBiTec/Results/HeavyMetals"
| Line 119: | Line 119: | ||
</br></br> | </br></br> | ||
| + | <!-- Einfluss von Kupfer auf den Zellextrakt --> | ||
<figure style="width: 600px"> | <figure style="width: 600px"> | ||
<a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2015/3/37/Bielefeld-CeBiTec_Influence_of_copper_on_the_cell_extract.jpeg" data-lightbox="heavymetals" data-title="Influence of different copper concentrations on our crude cell extract. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three biological replicates."><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2015/3/37/Bielefeld-CeBiTec_Influence_of_copper_on_the_cell_extract.jpeg" alt="Adjusting the detection limit"></a> | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2015/3/37/Bielefeld-CeBiTec_Influence_of_copper_on_the_cell_extract.jpeg" data-lightbox="heavymetals" data-title="Influence of different copper concentrations on our crude cell extract. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three biological replicates."><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2015/3/37/Bielefeld-CeBiTec_Influence_of_copper_on_the_cell_extract.jpeg" alt="Adjusting the detection limit"></a> | ||
| Line 124: | Line 125: | ||
</figure> | </figure> | ||
| − | + | <!-- Induktion mit Kupfer im Kupfer spezifischen Extrakt --> | |
<figure style="width: 600px"> | <figure style="width: 600px"> | ||
<a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2015/4/45/Bielefeld-CeBiTec_induction_copper_in_CueR_cell-extract.jpeg" data-lightbox="heavymetals" data-title="Copper specific cell extract made from <i>E. coli</i> cells which have already expressed the activator before cell extract production. Induction of copper inducible promoter without T7 in front of the operator site with different copper concentrations. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three biological replicates. "><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2015/4/45/Bielefeld-CeBiTec_induction_copper_in_CueR_cell-extract.jpeg" alt="Adjusting the detection limit"></a> | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2015/4/45/Bielefeld-CeBiTec_induction_copper_in_CueR_cell-extract.jpeg" data-lightbox="heavymetals" data-title="Copper specific cell extract made from <i>E. coli</i> cells which have already expressed the activator before cell extract production. Induction of copper inducible promoter without T7 in front of the operator site with different copper concentrations. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three biological replicates. "><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2015/4/45/Bielefeld-CeBiTec_induction_copper_in_CueR_cell-extract.jpeg" alt="Adjusting the detection limit"></a> | ||
| Line 130: | Line 131: | ||
</figure> | </figure> | ||
| − | + | <!--obrige Abbildung durch den errechneten Korrekturfaktor angepasst, da verschiedene Faktoren auf Zellextrakt wirken und so diesen beeinflussen.--> | |
<figure style="width: 600px"> | <figure style="width: 600px"> | ||
<a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2015/4/4c/Bielefeld-CeBiTec_correction_induction_copper_in_cueR_cell-extract.jpeg" data-lightbox="heavymetals" data-title="Copper specific cell extract made from <i>E. coli</i> cells which have already expressed the activator before cell extract production. Induction of copper inducible promoter without T7 in front of the operator site with different copper concentrations. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three biological replicates. Data are normalized on coppers influence to the cell extract."><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2015/4/4c/Bielefeld-CeBiTec_correction_induction_copper_in_cueR_cell-extract.jpeg" alt="Adjusting the detection limit"></a> | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2015/4/4c/Bielefeld-CeBiTec_correction_induction_copper_in_cueR_cell-extract.jpeg" data-lightbox="heavymetals" data-title="Copper specific cell extract made from <i>E. coli</i> cells which have already expressed the activator before cell extract production. Induction of copper inducible promoter without T7 in front of the operator site with different copper concentrations. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three biological replicates. Data are normalized on coppers influence to the cell extract."><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2015/4/4c/Bielefeld-CeBiTec_correction_induction_copper_in_cueR_cell-extract.jpeg" alt="Adjusting the detection limit"></a> | ||
| Line 136: | Line 137: | ||
</figure> | </figure> | ||
| + | <!-- Es wurde auch das Konstrukt mit einen T7 davor eingesetzt, es zeichen sich unterschhiede inder Flurescens ausbeute, so mit ist für das CFPS system ein vorgeschalteter T7 sinnvoll zur besseren sensitivität des Systems. --> | ||
<figure style="width: 600px"> | <figure style="width: 600px"> | ||
<a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2015/c/ce/Bielefeld-CeBiTec_induction_T7-copAP_copper_in_cueR_cell-extract.jpeg" data-lightbox="heavymetals" data-title="Copper specific cell extract made from <i>E. coli</i> cells which have already expressed the activator before cell extract production. Induction with different copper concentrations. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three biological replicates."><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2015/c/ce/Bielefeld-CeBiTec_induction_T7-copAP_copper_in_cueR_cell-extract.jpeg" alt="Adjusting the detection limit"></a> | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2015/c/ce/Bielefeld-CeBiTec_induction_T7-copAP_copper_in_cueR_cell-extract.jpeg" data-lightbox="heavymetals" data-title="Copper specific cell extract made from <i>E. coli</i> cells which have already expressed the activator before cell extract production. Induction with different copper concentrations. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three biological replicates."><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2015/c/ce/Bielefeld-CeBiTec_induction_T7-copAP_copper_in_cueR_cell-extract.jpeg" alt="Adjusting the detection limit"></a> | ||
| Line 141: | Line 143: | ||
</figure> | </figure> | ||
| + | <!-- auch dieses Abbildung wurde mit dem Korrekturfaktor korrigiert--> | ||
<figure style="width: 600px"> | <figure style="width: 600px"> | ||
<a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2015/0/01/Bielefeld-CeBiTec_correction_induction_T7-copAP_in_cueR_cell-extract.jpeg" data-lightbox="heavymetals" data-title="TEXT Error bars represent the standard deviation of three biological replicates."><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2015/0/01/Bielefeld-CeBiTec_correction_induction_T7-copAP_in_cueR_cell-extract.jpeg" alt="Adjusting the detection limit"></a> | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2015/0/01/Bielefeld-CeBiTec_correction_induction_T7-copAP_in_cueR_cell-extract.jpeg" data-lightbox="heavymetals" data-title="TEXT Error bars represent the standard deviation of three biological replicates."><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2015/0/01/Bielefeld-CeBiTec_correction_induction_T7-copAP_in_cueR_cell-extract.jpeg" alt="Adjusting the detection limit"></a> | ||
Revision as of 12:40, 14 September 2015
Heavy Metals
Zusammenfassung in ganz wenigen Worten.

Arsenic
in vivo

in vitro
Chromium
in vivo
Our sensor for chromium detection consists of ChrB the repressor and the chromate specific promoter ChrP. The promoter is regulated by the ChrB, which binds Cr-ions. Behind the promoter is a sfGFP for detection of a fluorescence signal. In vivo we could show that the addition of different concentrations of chromium have different effects to transcription of sfGFP.

in vitro





Copper
in vivo
Our sensor for copper detection consists of CueR a MerR like activator and the copper specific promoter CopAP. The promoter is regulated by CueR, which binds Cu2+-ions. We also used a sfGFP behind the promoter for detection trough a fluorescence signal.

in vitro





Lead
in vivo


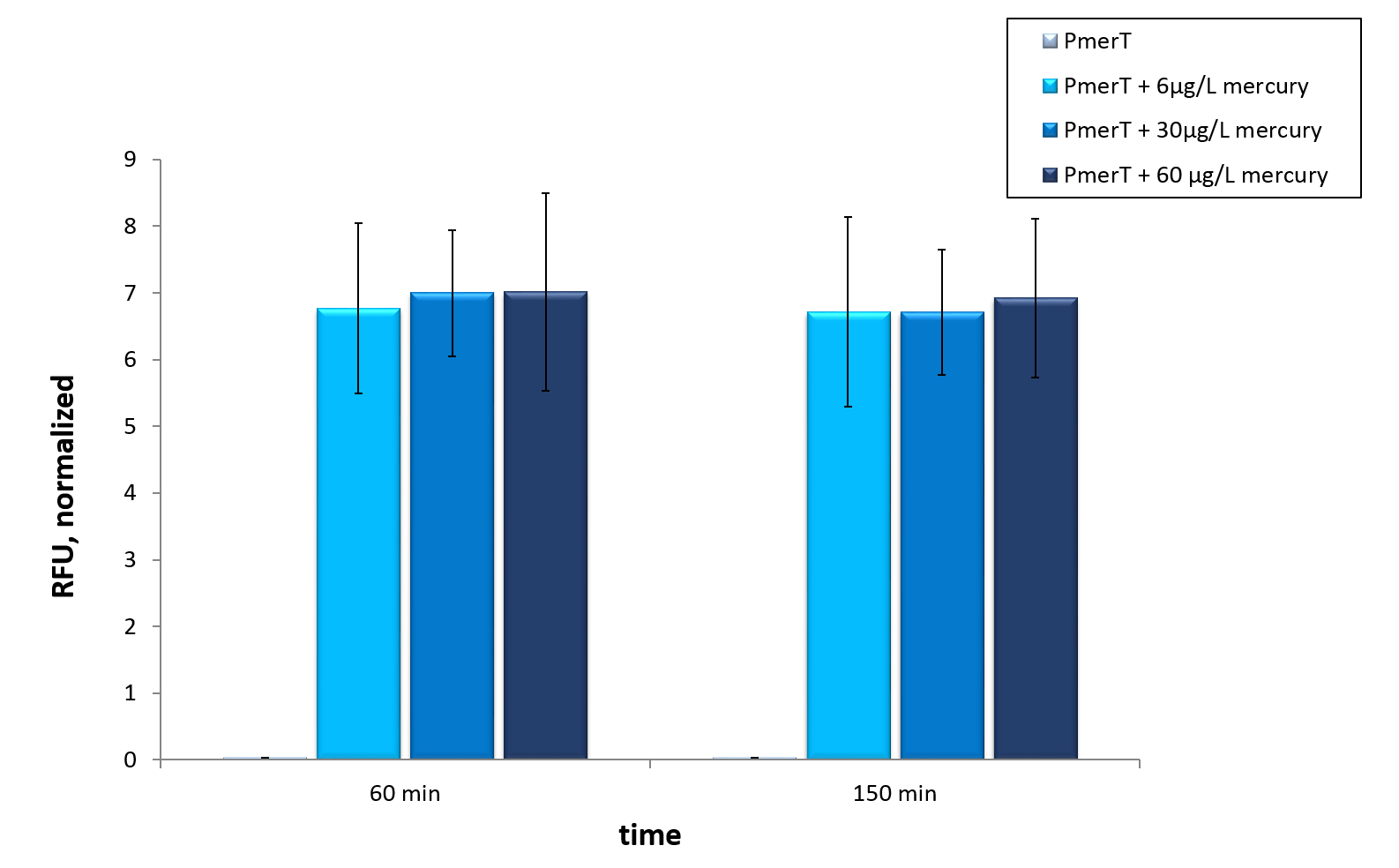
Mercury
in vivo


in vitro



Nickel
in vivo



