Difference between revisions of "Team:Bielefeld-CeBiTec/Results/HeavyMetals"
| Line 73: | Line 73: | ||
<h2><i>in vitro</i></h2> | <h2><i>in vitro</i></h2> | ||
| + | <!--Chrom bei niedrigeren Konzentrationen keinen signifikaten einfluss auf das System selbst, erst bei hoher Konzentration zeigt sich das CFPS nicht mehr in der lage ist ein Fluorescence signal zu erzeugen, zeigt, dass einen zu hohe konzentration das System zerstört. die Translations bzw Transskriptions ... sind nicht mehr in der Lage zu arbeiten, also keine | ||
<figure style="width: 600px"> | <figure style="width: 600px"> | ||
<a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2015/9/99/Bielefeld-CeBiTec_Influence_of_chromium_on_the_cell_extract.jpeg" data-lightbox="heavymetals" data-title=" Influence of different chromium concentrations on our crude cell extract. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three biological replicates."><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2015/9/99/Bielefeld-CeBiTec_Influence_of_chromium_on_the_cell_extract.jpeg" alt="Adjusting the detection limit"></a> | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2015/9/99/Bielefeld-CeBiTec_Influence_of_chromium_on_the_cell_extract.jpeg" data-lightbox="heavymetals" data-title=" Influence of different chromium concentrations on our crude cell extract. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three biological replicates."><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2015/9/99/Bielefeld-CeBiTec_Influence_of_chromium_on_the_cell_extract.jpeg" alt="Adjusting the detection limit"></a> | ||
| Line 123: | Line 124: | ||
</br></br> | </br></br> | ||
| − | <!-- Einfluss von Kupfer auf den Zellextrakt --> | + | <!-- Einfluss von Kupfer auf den Zellextrakt, keinen negative Einfluss auf das CFPS so mit kann gezeigt werden dass dieses System relativ stabil gegenüber verschiedenen Kupferkonzentratione ist --> |
<figure style="width: 600px"> | <figure style="width: 600px"> | ||
<a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2015/3/37/Bielefeld-CeBiTec_Influence_of_copper_on_the_cell_extract.jpeg" data-lightbox="heavymetals" data-title="Influence of different copper concentrations on our crude cell extract. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three biological replicates."><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2015/3/37/Bielefeld-CeBiTec_Influence_of_copper_on_the_cell_extract.jpeg" alt="Adjusting the detection limit"></a> | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2015/3/37/Bielefeld-CeBiTec_Influence_of_copper_on_the_cell_extract.jpeg" data-lightbox="heavymetals" data-title="Influence of different copper concentrations on our crude cell extract. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three biological replicates."><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2015/3/37/Bielefeld-CeBiTec_Influence_of_copper_on_the_cell_extract.jpeg" alt="Adjusting the detection limit"></a> | ||
Revision as of 13:02, 14 September 2015
Heavy Metals
Zusammenfassung in ganz wenigen Worten.

Arsenic
in vivo

in vitro

Chromium
in vivo
Our sensor for chromium detection consists of ChrB the repressor and the chromate specific promoter ChrP. The promoter is regulated by the ChrB, which binds Cr-ions. Behind the promoter is a sfGFP for detection of a fluorescence signal. In vivo we could show that the addition of different concentrations of chromium have different effects to transcription of sfGFP.

in vitro





Lead
in vivo


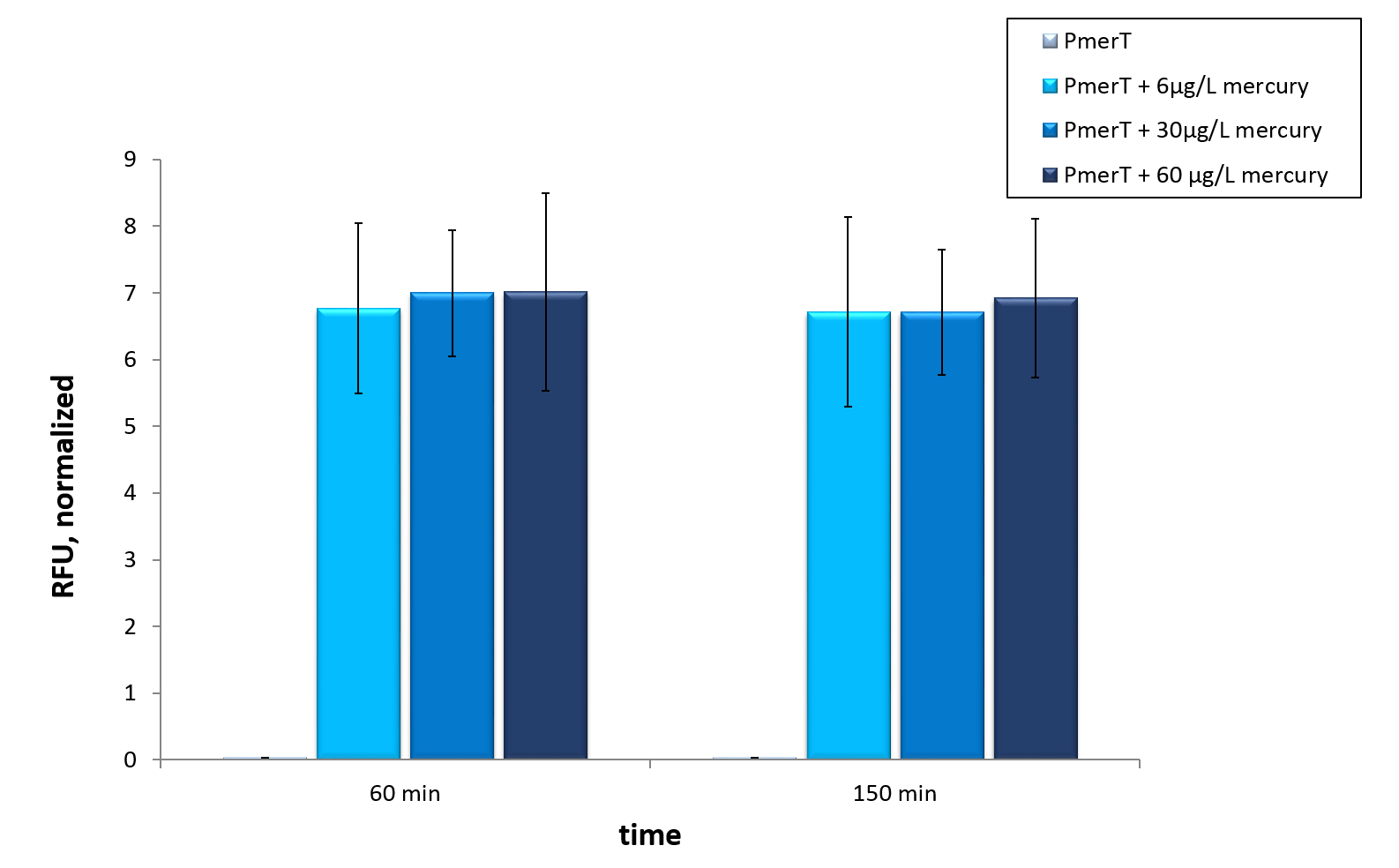
Mercury
in vivo


in vitro



Nickel
in vivo



